Serie
From Setup to Success: Navigating External Collaboration in Microsoft 365 Like a Pro
1: Introducing External Collaboration in Microsoft 365
2: Configuring External Collaboration in Microsoft 365 (Du liest diesen Artikel)
3: Best Practices for Managing B2B Guest Accounts in Microsoft 365
In our previous blog post, we discussed the important role of guest accounts in external collaboration within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. This post explores the various settings available to IT Administrators for controlling Business-to-Business (B2B) guest accounts in different tools and services.
Facilitating Collaboration with B2B Guest Accounts in Microsoft 365
B2B Guest Accounts in Microsoft 365 are crucial for collaboration with external partners. Key advantages include:
-
Seamless Collaboration with External Stakeholders: Guest accounts facilitate collaboration with individuals outside your organization, fostering teamwork on projects, document sharing, and participation in teams with clients, vendors, or other external collaborators.
-
Effortless Access to Shared Resources: Guests can effortlessly access shared resources such as files, documents, and calendars within your Microsoft 365 environment. This promotes smooth collaboration without the need for constant email communication.
-
Team Collaboration in Microsoft Teams: Integration with Microsoft Teams allows guests to actively engage in discussions, meetings, and collaborative file editing. This enhances communication and collaboration among team members, irrespective of their organizational affiliations.
-
Streamlined Identity Management: Guest accounts eliminate the need to create separate credentials for external collaborators. They can use their existing credentials from their own organizations, streamlining identity management and reducing administrative overhead.
-
Robust Security Measures: Microsoft 365 provides security features to manage guest access effectively. Administrators can control guest permissions, apply conditional access policies, and ensure that guest users meet specific security criteria before accessing sensitive information.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO) Convenience: Guests benefit from single sign-on capabilities, simplifying access to multiple Microsoft 365 services without the hassle of managing multiple sets of credentials.
-
Audit and Reporting Capabilities: Microsoft 365 offers robust auditing and reporting features, empowering administrators to monitor guest user activities and manage external collaboration securely.
-
Consistent User Experience: Guests enjoy a consistent user experience within Microsoft 365, ensuring ease of navigation and platform utilization regardless of their organizational affiliation.
While leveraging guest accounts brings numerous advantages, organizations must remain vigilant about security and compliance considerations. Proper configuration of permissions and access controls is essential to ensure that guest users only have necessary access to resources and data.
Distinguishing B2B Guest Accounts from Internal Members
To better comprehend the dynamics, it's crucial to differentiate between B2B Guest Accounts and internal members in Microsoft 365.
| Aspect | B2B Guest Accounts | Internal Members |
|---|---|---|
| Access Scope | Limited access to specified resources and collaborative elements for joint projects. | Broader access rights within the organization, covering internal systems, documents, and applications. |
| Identity Management | Retain original organizational identity and credentials without becoming part of the hosting organization's internal directory. | Fully integrated into the hosting organization's internal directory with specific user roles and permissions. |
| Collaboration Boundaries | Seamlessly collaborate with internal members within shared spaces, encouraging cross-organizational teamwork. | Interact within the organization's internal environment without the constraints of external collaboration. |
Lifecycle of a B2B Guest Account
The typical lifecycle of a B2B Guest Account involves the following steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Invitation | An internal member invites an external partner, specifying the resources or applications they need access to. |
| Acceptance | The B2B Guest Account accepts the invitation and completes necessary authentication processes. Based on the organization settings, the guest might be required to accept terms of use and configure multi-factor authentication. |
| Access Configuration | The hosting organization configures access rights, specifying permissions for required resources. This can be done on resources that are enabled for B2B Guest Accounts. |
| Collaboration | B2B Guest Accounts collaborate with internal members, contributing to projects, accessing shared documents, and participating in communication channels. |
| Expiration or Revocation | Access can expire after a set duration or be revoked at any time, ensuring control over external access. Permissions can either be removed on existing resources or a deletion of the B2B account can be performed having an offboarding process. |
| Offboarding | When collaboration concludes, access is terminated, maintaining security and compliance. Offboarding is done by deleting a B2B guest account from the hosting organization. |
Having established this foundation, let's delve into the configuration of B2B guest access in a hosting organization.
How do I configure B2B Guest Account settings?
At the core of external collaboration and sharing within Microsoft 365 is Entra ID, also known as Azure AD. It's crucial to understand that Entra ID's guest-sharing restrictions take precedence over any configurations set in other Microsoft 365 services. The Entra ID Settings for guest account management play a pivotal role in determining who can send invitations to external entities, who can be invited, and the basic permissions associated with guest accounts. Once a guest account is invited, additional services built upon Entra ID dictate how these accounts can access specific information in your environment.
To effectively manage guest user access, navigate to External Identities in Entra ID and explore the following settings. These settings specify who can invite whom in your organization:
Why Enabling Entra ID Integration for SharePoint Guest Sharing Matters
For tenants created before March 2023, SharePoint and OneDrive still use the legacy SharePoint-only guest model, where external users authenticate through email-based one-time passcodes (OTPs). This model operates outside Microsoft Entra ID governance and lacks Conditional Access, MFA, and compliance controls.
You can check and enable the modern integration directly from SharePoint Online Management Shell:
### Connect to SharePoint Online with an admin account
Connect-SPOService -Url https://<tenant>-admin.sharepoint.com
Get-SPOTenant | Select EnableAzureADB2BIntegration
# If the result shows:
EnableAzureADB2BIntegration : False
# You are still using the legacy guest model.
# To modernize and secure external collaboration, run:
Set-SPOTenant -EnableAzureADB2BIntegration $trueOnce enabled, SharePoint and OneDrive will automatically create Entra ID guest accounts for new sharing invitations, replacing OTP-based guests and bringing all external users under full Entra ID governance.
⚠️ Important: Enabling this setting may invalidate existing links shared with legacy guests until they are reshared or those users are invited into Entra ID. Before enabling, export existing SharePoint guests, prepare a migration plan, and inform affected users.
By enabling Entra ID integration, organizations gain a unified and secure framework for managing external collaboration. It enforces MFA and Conditional Access policies for all guest accounts, centralizes identity and lifecycle management in Entra ID, and ensures consistent auditing and compliance visibility across Microsoft 365. In addition, it provides a seamless single sign-on experience with MFA trust between tenants, reducing login friction for external users. Most importantly, this change aligns older tenants with Microsoft’s modern B2B collaboration model, ensuring compatibility with future features and long-term security best practices.
Controlling Visibility for Guest Accounts
This setting primarily serves to regulate the visibility of content within your directory for guest accounts. The majority of our customers either adhere to the default configuration or opt to enhance security by imposing more stringent visibility restrictions on guest accounts.
| Access Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Equal Access to Microsoft Entra Resources | Guests enjoy the same access as members, providing comprehensive entry to Microsoft Entra resources. |
| Limited Access (Default) | Guests have restricted access to specific directory tasks but can view non-hidden group memberships. |
| Restricted Access | The most restrictive setting allows guests access solely to their profiles, prohibiting viewing other profiles, groups, or memberships. Under restricted access, guests can only view their profiles. |
Controlling Guest Invitations
| Invitation Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Anyone in the Organization (Most Inclusive) | All users, including guests and non-admins, can invite external users. |
| Member Users and Users with Specific Admin Roles (Default) | Designated users with admin roles can invite guests with member permissions. |
| Only Users with Specific Admin Roles | Only users with administrator roles can invite guests. |
| No One in the Organization (Most Restrictive) | Deny everyone in the organization from inviting guests. |
This setup decides who can invite people as guests. It's a crucial first step in managing the life cycle of accounts. Before letting a guest access things in an organization, we need to get this right. Usually, organizations stick to the default settings for guest accounts. But I think only internal users should control access to internal stuff. So, I suggest not using the setting Anyone in the Organization (Most Inclusive) to keep things more secure.
Some organizations do not want to invite guest accounts at all. You can control this with No One in the Organization (Most Restrictive). This means no one can add new guest accounts, but it doesn't affect the ones already there.
Some organizations prefer to manage guest account invitations through an approval or data collection process. To achieve this, you can utilize the Only Users with Specific Admin Roles feature and then set up the desired process. EasyLife 365 also supports these types of scenarios.
Allowing or Blocking Domains
Admins have the power to control which email domains are allowed or not when inviting guests. This helps create a safe and customized collaboration space for external partners.
This feature is handy when you want to limit guest invites to certain domains, preventing invites from, let's say, specific email addresses (e.g. gmail.com). You can tweak this to match your organization's security and collaboration needs, like keeping guest accounts specific to certain organizations or domains.
Configuring Sharing Settings for Documents and Sites
Enhanced Text:
SharePoint sharing settings play a pivotal role in governing content sharing across OneDrive and SharePoint Online. Notably, Microsoft Teams and Viva Engage leverage SharePoint Online as their file storage system. Consequently, the sharing settings for files and sites also impact the sharing mechanisms within these collaborative resources. These settings can be specified either at the tenant level or on an individual site basis, with tenant settings taking precedence over site-specific ones.
To configure organization-level sharing settings in SharePoint, follow these steps:
- Access the SharePoint admin center.
- Navigate to "Policies" and select "Sharing."
- Verify the external sharing settings for SharePoint or OneDrive.
- If modifications are made, click "Save" to apply the updated settings.
A noteworthy feature is the use of "Anyone" links, allowing the sharing of files and folders through anonymous links without authentication. It's essential to manage the default expiration date for these links on the same settings page.
For those opting not to use anonymous links, it is advisable to configure settings to at least "New and existing guests" or a lower tier.
Consider the following scenarios:
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| New and existing guests | Utilize this setting to extend invitations to new guest accounts, even if the guest has not been invited within your organization. This assumes that sharing settings in Entra ID are open for your members or guests. |
| Existing guests | This setting is applicable when you only want to grant access to individuals who have been added to your directory. For organization-managed members, this process is typically automated. However, guest accounts need to be invited to your organization before gaining access to a specific site, folder, or file. |
| Only people in your organization | Opt for this option to restrict a site exclusively for internal use. |
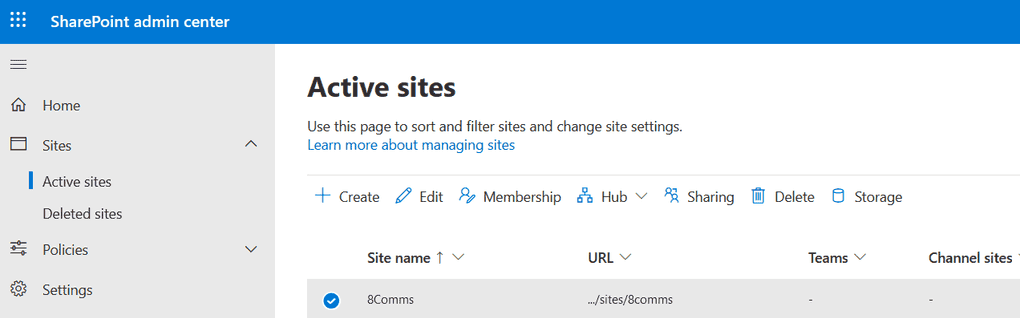
These settings extend beyond file and folder sharing, also governing access to individual SharePoint sites. They can be customized at both organizational and site levels, with individual site configurations constrained by the more permissive organizational settings. Best practices recommend maintaining organization-level settings aligned with your specific use case.
For site-level sharing settings, navigate to the "Active sites" tab, select your desired site, and configure the sharing settings accordingly.
Control Access in Microsoft 365 Groups and Teams
Modern SharePoint sites leverage Microsoft 365 Groups for access control. Enable Microsoft 365 Groups guest settings to facilitate guest access in groupified SharePoint sites, Microsoft Teams, and Microsoft 365 Groups. Guests invited to a Group gain contribution rights on all underlying services associated with the Microsoft 365 Group if no other setting is specified.
Follow these steps to set Microsoft 365 Groups guest settings:
- In the Microsoft 365 admin center, navigate to Settings > Org settings.
- Access Microsoft 365 Groups and ensure the necessary checkboxes are selected if you want to enable guest accounts for these resources.
You have the flexibility to manage these settings for individual Groups using PowerShell or Sensitivity Labels, provided that global settings are enabled. Typically, default settings remain open at the tenant level, with permissions restricted based on sensitivity or automated tools like EasyLife during provisioning.
Teams Guest Access Settings
Microsoft 365 Teams uses Microsoft 365 Groups as a basis for its services. You can control with an on/off switch if guest access is allowed to the Teams platform. The individual guest account access can be controlled using PowerShell and Sensitivity Labels by changing the settings on a Microsoft Group level.
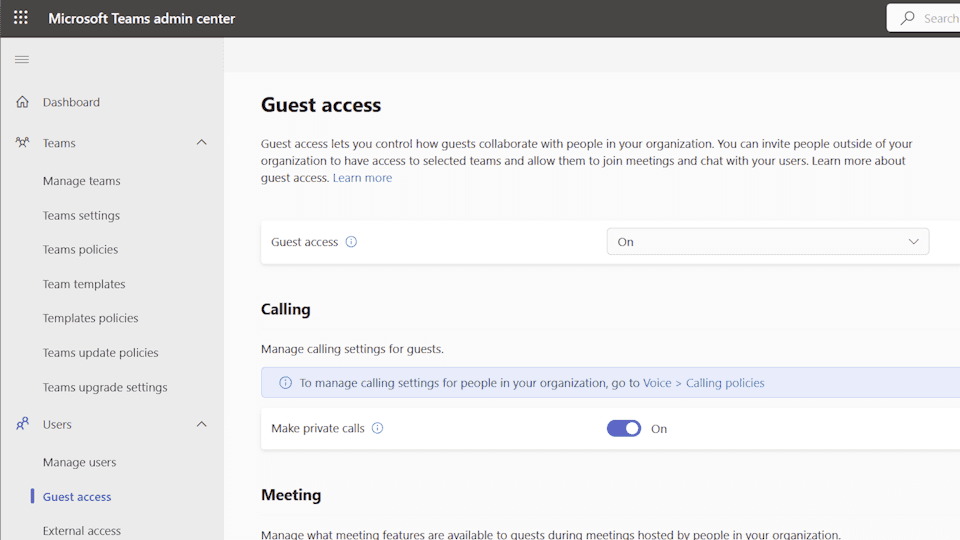
You can enable/disable guest access to Teams using these steps.
- In the Teams admin center, navigate to Users > Guest access.
- Ensure Guest access is set to On.
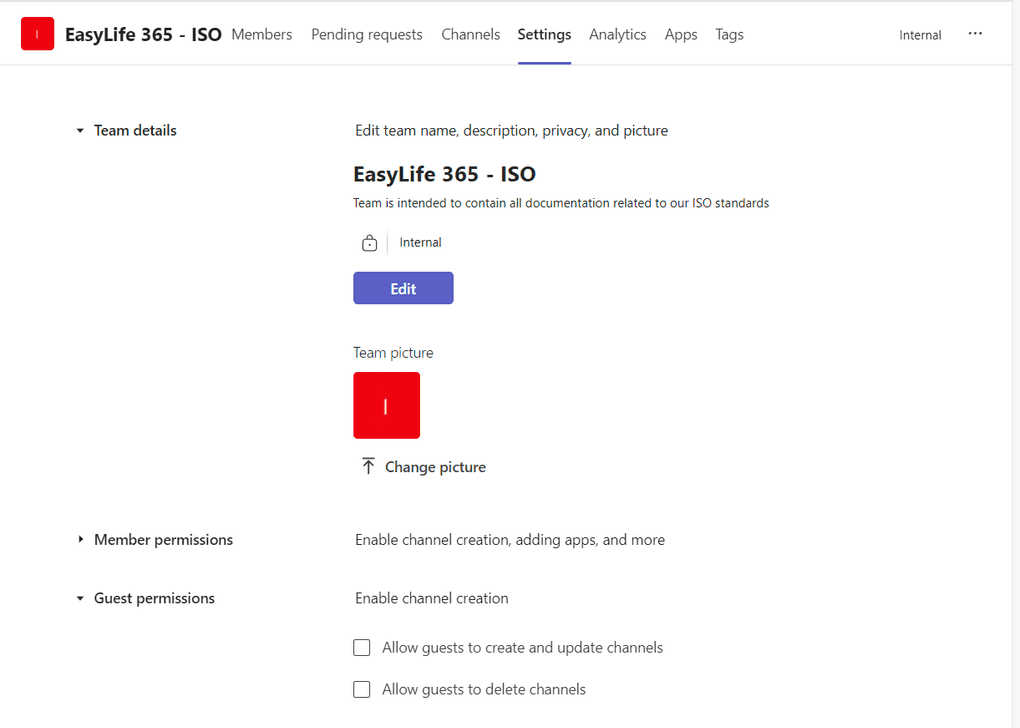
Team channel guest permissions
Guests in a team have fewer capabilities than team members, but they can still contribute in channels where the actual work takes place. Team owners can manage guest permissions for channels by accessing the Teams settings. They can do this by selecting the Teams button, navigating to the team name, clicking More options, and choosing Manage team. From there, they can go to Settings > Guest permissions and adjust the permissions as needed.
Wrapping It Up
In conclusion, we have delved into the essential settings for controlling the addition of guest accounts within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, specifically focusing on the initial stages of the guest account life cycle. By understanding and configuring aspects such as visibility, invitation controls, domain restrictions, and sharing settings, organizations can establish a secure and efficient environment for external collaboration.
This discussion primarily addressed the invitation and redemption phases of the guest account life cycle, emphasizing the importance of proper configuration to ensure security, compliance, and streamlined collaboration. As we navigate through the intricate landscape of managing guest accounts, it's crucial to recognize that this is just the beginning.
In subsequent blog posts, we will further explore additional life cycle topics and delve into best practices for effectively managing guest accounts throughout their entire journey. From access configuration to collaboration, expiration or revocation, and eventual offboarding, we will provide insights and guidance to help organizations optimize their external collaboration processes while maintaining robust security measures. Stay tuned for more insights and practical tips on maximizing the potential of guest accounts in Microsoft 365.
This post is part of a post series about B2B Guest Account management.
- Introduction
- Configuration (this post)